Birth Marks
Birth Marks
Unveiling the Secrets of Moles: Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
Introduction
Moles, medically known as nevi, are common skin growths that can appear in various shapes, sizes, and colors. While most moles are harmless and simply a cosmetic concern, some can develop into malignant melanomas, a serious form of skin cancer. Understanding the causes, types, and treatment options for moles is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and ensuring early detection of potential skin cancer. This article provides comprehensive information on the nature of moles, the factors contributing to their development, the different types, and the various treatment methods available. By the end, readers will have a thorough understanding of moles and be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their skin health.
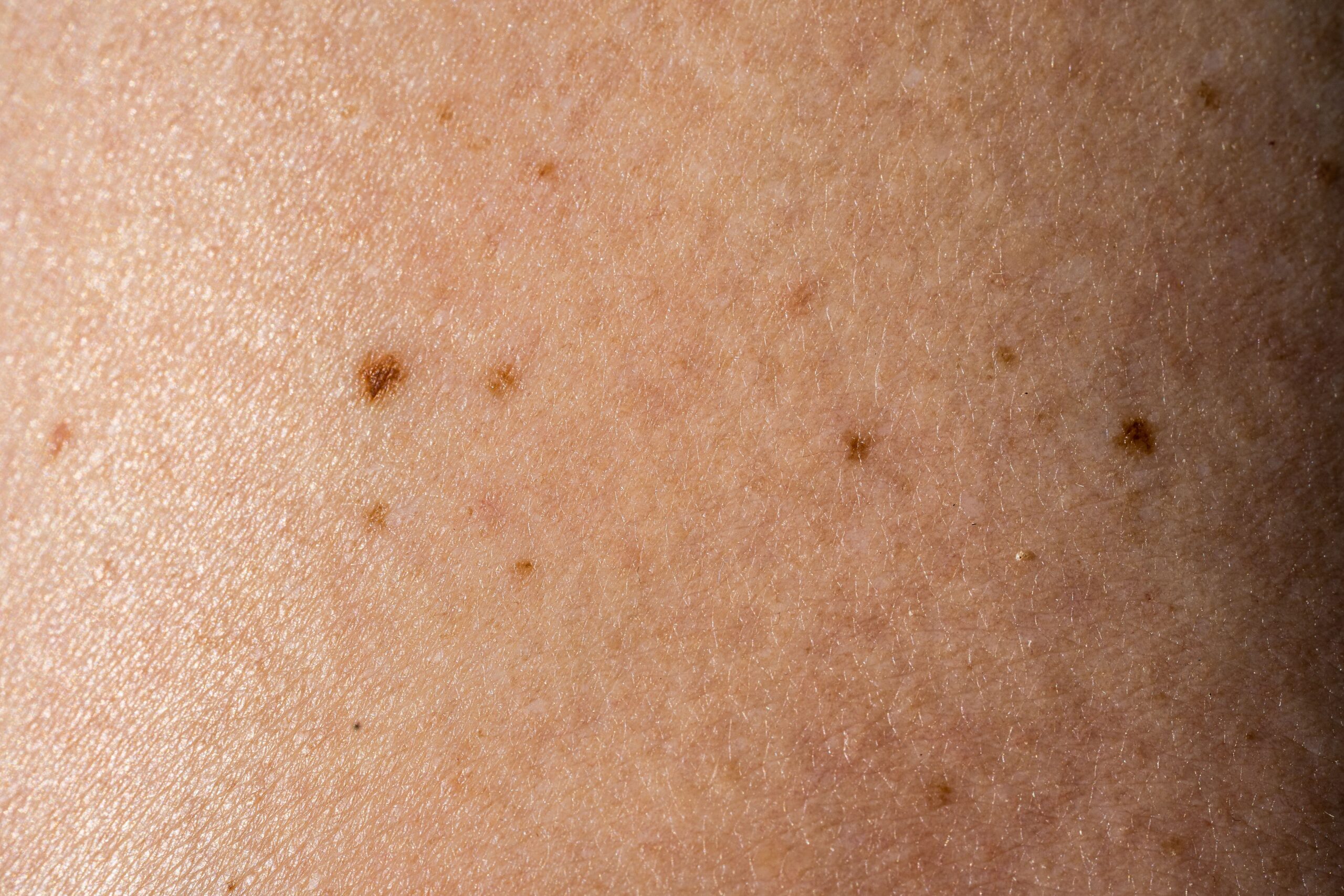
What are Moles?
Moles are clusters of pigmented cells that can appear anywhere on the skin. They are usually brown or black but can also be blue, red, or flesh-colored. Moles can be flat or raised, smooth or rough, and may have hair growing from them. They form due to the growth of melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigment. Genetics and environmental factors, particularly sun exposure, play significant roles in their development. For instance, Sarah noticed a small, brown spot on her arm that had been there since childhood. Over the years, it remained unchanged, illustrating a typical benign mole.
Causes of Moles
Several factors contribute to the development of moles, including genetic predisposition, sun exposure, and hormonal changes. Understanding these causes can help in preventing the formation of new moles and managing existing ones. For example, John’s family had a history of moles, and he developed several during his teenage years, particularly after spending a lot of time outdoors without adequate sun protection.
Types of Moles
Moles can be classified into several types based on their appearance and potential risk. Common moles, atypical moles, congenital moles, and acquired moles are the main categories. Each type has unique characteristics. For example, Maria was born with a large, brown mole on her back, known as a congenital nevus. While it posed no immediate risk, her dermatologist recommended regular check-ups to monitor any changes.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Early detection of potentially malignant moles is key to preventing skin cancer. Various methods of mole examination include self-examination, dermatoscopy, and biopsy. The ABCDEs of melanoma detection—Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolving—are crucial for identifying suspicious moles. During a routine skin check, Lisa’s dermatologist used a dermatoscope to examine a mole with irregular borders and multiple colors, leading to a biopsy that revealed an early-stage melanoma.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Not all moles require surgical removal. Non-surgical treatments such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, and topical medications are available. These options are particularly useful for cosmetic removal or treating non-cancerous moles. For instance, James opted for laser therapy to remove a mole on his face that bothered him cosmetically. The procedure was quick, and he was pleased with the results.
Surgical Treatment Options
When moles are suspicious or confirmed to be cancerous, surgical removal is often necessary. Various surgical techniques include excision, shave removal, and Mohs surgery. The recovery process and potential complications are also important considerations. After a mole on Emma’s leg was diagnosed as melanoma, she underwent Mohs surgery to ensure all cancerous cells were removed while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
Preventing Moles and Skin Cancer
Prevention is better than cure. Strategies to prevent the formation of new moles and reduce the risk of skin cancer include sun protection, regular skin checks, and lifestyle modifications. Mark adopted a diligent sun protection routine, including using broad-spectrum sunscreen and wearing protective clothing, significantly reducing his number of new moles.
Living with Moles
For many people, living with moles is a normal part of life. Common concerns include cosmetic issues, changes during pregnancy, and the psychological impact of visible moles. Despite having several moles on her face, Jane embraced her unique appearance and found confidence through a supportive online community.
Myths and Facts About Moles
There are many misconceptions about moles. Debunking common myths and providing factual information helps distinguish between folklore and science. For example, contrary to the myth that removing a mole can cause cancer, the truth is that properly removing a suspicious mole can prevent cancer.
Future Research and Developments
The field of dermatology is constantly evolving. Recent advancements in mole research and potential future developments in treatment and prevention are promising. For example, recent studies have explored the use of artificial intelligence in mole analysis, promising more accurate and early detection of malignant changes.
Conclusion
Understanding moles is essential for maintaining skin health and preventing serious conditions like melanoma. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to the causes, types, and treatment options for moles, equipping readers with the knowledge to manage their skin effectively. Regular self-examinations and professional check-ups are crucial for early detection and treatment of any suspicious moles. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can ensure their skin remains healthy and free from potential harm.
FAQ's
Yes, some moles can fade or disappear over time, but any changes should be monitored by a dermatologist.
While some natural remedies are claimed to remove moles, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before trying them, as improper removal can lead to complications.
It's recommended to perform monthly self-examinations and have a professional skin check at least once a year, or more frequently if you have risk factors for skin cancer.